
内置命令包含在 bash shell 本身里面。我该如何在 Linux / Apple OS X / *BSD / Unix 类操作系统列出所有的内置 bash 命令,而不用去读大篇的 bash 操作说明页?
shell 内置命令就是一个命令或一个函数,从 shell 中调用,它直接在 shell 中执行。 bash shell 直接执行该命令而无需调用其他程序。你可以使用 help 命令查看 Bash 内置命令的信息。以下是几种不同类型的内置命令。
内置命令的类型
- Bourne Shell 内置命令:内置命令继承自 Bourne Shell。
- Bash 内置命令:特定于 Bash 的内置命令表。
- 修改 Shell 行为:修改 shell 属性和可选行为的内置命令。
- 特别的内置命令:由 POSIX 特别分类的内置命令。
如何查看所有 bash 内置命令
有以下的命令:
$ help
$ help | less
$ help | grep read
样例输出:
GNU bash, version 4.1.5(1)-release (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)
These shell commands are defined internally. Type `help' to see this list.
Type `help name' to find out more about the function `name'.
Use `info bash' to find out more about the shell in general.
Use `man -k' or `info' to find out more about commands not in this list.
A star (*) next to a name means that the command is disabled.
job_spec [&] history [-c] [-d offset] [n] or hist>
(( expression )) if COMMANDS; then COMMANDS; [ elif C>
. filename [arguments] jobs [-lnprs] [jobspec ...] or jobs >
: kill [-s sigspec | -n signum | -sigs>
[ arg... ] let arg [arg ...]
[[ expression ]] local [option] name[=value] ...
alias [-p] [name[=value] ... ] logout [n]
bg [job_spec ...] mapfile [-n count] [-O origin] [-s c>
bind [-lpvsPVS] [-m keymap] [-f filen> popd [-n] [+N | -N]
break [n] printf [-v var] format [arguments]
builtin [shell-builtin [arg ...]] pushd [-n] [+N | -N | dir]
caller [expr] pwd [-LP]
case WORD in [PATTERN [| PATTERN]...)> read [-ers] [-a array] [-d delim] [->
cd [-L|-P] [dir] readarray [-n count] [-O origin] [-s>
command [-pVv] command [arg ...] readonly [-af] [name[=value] ...] or>
compgen [-abcdefgjksuv] [-o option] > return [n]
complete [-abcdefgjksuv] [-pr] [-DE] > select NAME [in WORDS ... ;] do COMM>
compopt [-o|+o option] [-DE] [name ..> set [--abefhkmnptuvxBCHP] [-o option>
continue [n] shift [n]
coproc [NAME] command [redirections] shopt [-pqsu] [-o] [optname ...]
declare [-aAfFilrtux] [-p] [name[=val> source filename [arguments]
dirs [-clpv] [+N] [-N] suspend [-f]
disown [-h] [-ar] [jobspec ...] test [expr]
echo [-neE] [arg ...] time [-p] pipeline
enable [-a] [-dnps] [-f filename] [na> times
eval [arg ...] trap [-lp] [[arg] signal_spec ...]
exec [-cl] [-a name] [command [argume> true
exit [n] type [-afptP] name [name ...]
export [-fn] [name[=value] ...] or ex> typeset [-aAfFilrtux] [-p] name[=val>
false ulimit [-SHacdefilmnpqrstuvx] [limit>
fc [-e ename] [-lnr] [first] [last] o> umask [-p] [-S] [mode]
fg [job_spec] unalias [-a] name [name ...]
for NAME [in WORDS ... ] ; do COMMAND> unset [-f] [-v] [name ...]
for (( exp1; exp2; exp3 )); do COMMAN> until COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
function name { COMMANDS ; } or name > variables - Names and meanings of so>
getopts optstring name [arg] wait [id]
hash [-lr] [-p pathname] [-dt] [name > while COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
help [-dms] [pattern ...] { COMMANDS ; }
另外一种选择是使用下列命令:
compgen -b
compgen -b | more
查看 Bash 的内置命令信息
运行以下得到详细信息:
help command
help read
要仅得到所有带简短描述的内置命令的列表,执行如下:
$ help -d
查找内置命令的语法和其他选项
使用下列语法去找出更多的相关内置命令:
help name
help cd
help fg
help for
help read
help :
样例输出:
:: :
Null command.
No effect; the command does nothing.
Exit Status:
Always succeeds
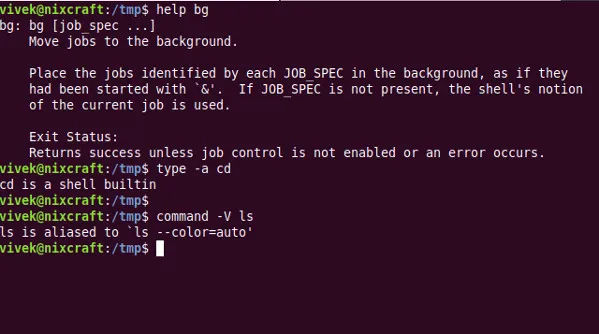
找出一个命令是内部的(内置)还是外部的
使用 type 命令或 command 命令:
type -a command-name-here
type -a cd
type -a uname
type -a :
type -a ls
或者:
type -a cd uname : ls uname
样例输出:
cd is a shell builtin
uname is /bin/uname
: is a shell builtin
ls is aliased to `ls --color=auto'
ls is /bin/ls
l is a function
l ()
{
ls --color=auto
}
或者:
command -V ls
command -V cd
command -V foo
关于作者
作者是 nixCraft 网站的发起人和经验丰富的系统管理员,以及 Linux 操作系统/Unix shell 脚本编程培训师。他与全球客户以及包括 IT、教育、国防和空间研究以及非营利部门在内的各个行业合作。可以在 Twitter、Facebook、 Google+ 上关注他。
via: https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/linux-unix-bash-shell-list-all-builtin-commands/
作者:Vivek Gite 译者:KarenMrzhang 校对:wxy


发表回复